Parameter Definition
Strategy logic parameters
- upperPrice
- lowerPrice
- currentPrice
- gridStep
- gridAmount
- initPrice
- initAmount
- totalGrids
- tarPos
- baseCurrency
- quoteCurrency
Strategy performance calculation
- startPrice
- initBase
- initQuote
- finalBase
- finalQuote
- initDate
- unilateral
- posAvg
- totalDays
What’s grid trading
Strategy usage background: after a big bullish market, the market starts to go bearish,
that’s the right moment for using grid trading strategy.
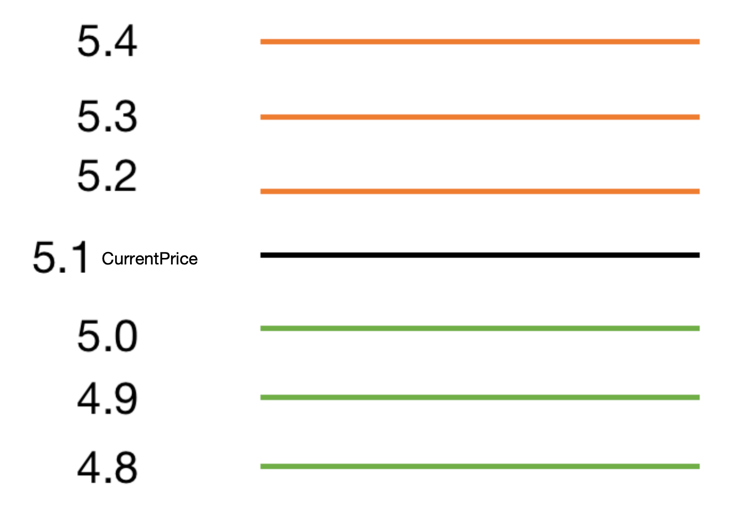 Just like the graph above, the green lines stand for buy limit orders, red lines stand for sell limit orders.
The grid trading is just placing orders based on the current price, places sell orders at prices that
are higher than current price, places buy orders at prices that are lower than current price.
Just like the graph above, the green lines stand for buy limit orders, red lines stand for sell limit orders.
The grid trading is just placing orders based on the current price, places sell orders at prices that
are higher than current price, places buy orders at prices that are lower than current price.
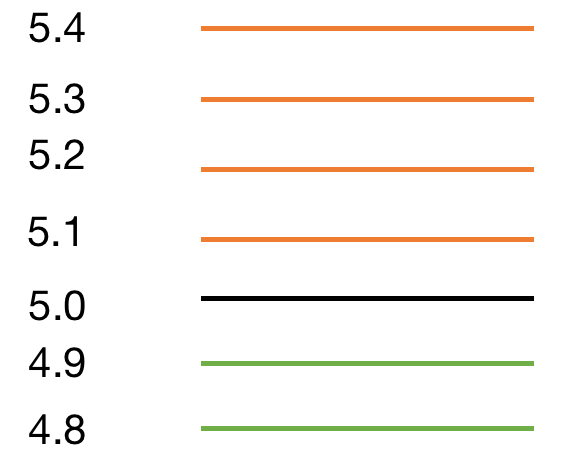 Assume that the price drop to 5, the limit buy order at 5 would be executed, we replenish another sell order
at 5.1, the orders list would like the above graphs. The reverse situation would be the same,
so during a market where the volatility is high, this strategy can generate profit.
Assume that the price drop to 5, the limit buy order at 5 would be executed, we replenish another sell order
at 5.1, the orders list would like the above graphs. The reverse situation would be the same,
so during a market where the volatility is high, this strategy can generate profit.
Spot grid trading parameters
The basic parameters from spot grid trading are :
- Upper and lower limit. e.g. [1500 ~ 3000]
- Grid gap. can be proportional 1 %, or a fixed number such as 50
- Total asset invested. The number of quote asset that’s invested, such as 1000 usdc
- Grid type. Place same number of quote asset at each grid or same number of base asset
Spot grid strategy by default doesn’t have leverage. In the condition where we don’t lend any asset, the strategy needs to have a clear upper and lower limit. For example, the coin pair ETHUSDT sitting at current price at 2000, we would assume that the price would fluctuate in between 1500 and 3000. Notice that if the price reaches upper limit then all we have are the quote asset USDT, the reverse situation would be the base asset ETH.
After determining the upper and lower bounds, we can calculate the total number of grids based on the grid interval. After calculating the total number of grids, we can calculate the amount of pending orders or the number of coins in each grid. There are two calculation methods, corresponding to arithmetic grids and geometric grids.
Arithmetic grids and Geometric grids
- Arithmetic grids totalGrids = (upperPrice - lowerPrice) / gridStep gridAmount = initAmount / totalGrids
- Geometric grids totalGrids = log(upperPrice/lowerPrice)/log(1 + gridStep) gridAmount = initAmount / totalGrids
What is the price pivot and target position
Note that since the upper and lower bounds as well as the investment amount are fixed, we can actually calculate the ratio of base to quote at any given price, and since base can be thought of as our position and quote as our money, we can calculate the ratio of our position at any given price.
It is worth noting that when the price is at the price pivot, as shown in the figure below,
the value of the base and the quote are equal, i.e., they are in the state of “half-position”, with a value of (initAmount/2), or,
in other words, the price at which the position is in the state of half-position is the price pivot,
and the price is the price at which the position is in the state of half-position,
and the price is the price pivot. When the price oscillates around the price pivot,
it is the ideal state for the strategy, because there are im losses.
 The following pivot price is calculated:
The following pivot price is calculated:
- Arithmetic grids initPrice = (upperPrice + lowerPrice)/2
- Geometric grids initPrice = exp(0.5 * log(upperPrice*lowerPrice))
Here is how we calculate the target position:
- Arithmetic grids tarPos = (initPrice - currentPrice)/gridStep * gridAmount + initAmount/2
- Geometric grids tarPos = log(initPrice/currentPrice)/log(1 + gridStep)*gridAmount + initAmount/2
Impermanent loss and performance calculation
First, let’s look at the components of performance:
- Based on the price
Total performance = profit and loss caused by currency price fluctuations + profit and loss caused by transactions = current assets - initial assets / initial assets * 100% The profit and loss caused by currency price fluctuations is what we call impermanent loss.
- Based on the strategy
Total performance = Impermanent loss profit and loss + Number of transactions (take the side with less total number of buy and sell orders) * Grid interval * Grid order amount
Impermanent loss: from startPrice to currentPrice, assuming that the price does not fluctuate during the period, How much loss will the trades made by the strategy bring to the total net value.
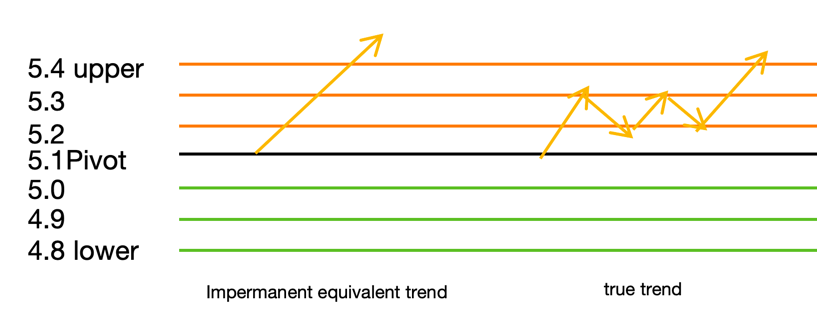 The price climbed from 5.0 to 5.4. If we do not run the strategy, the
rate of return is (5.4 - 5) / 5 = 8%. Assuming that we run the strategy, we
have been selling our positions when the price rises. After 5.4, according
to the above figure, the impermanent loss equivalent trend has executed 3
sell orders. The total assets are lower than the total assets without running
the strategy. The rate of return must be less than 8%. This is the so-called
“less profit”, and the less profit is what we call impermanent loss.
The price climbed from 5.0 to 5.4. If we do not run the strategy, the
rate of return is (5.4 - 5) / 5 = 8%. Assuming that we run the strategy, we
have been selling our positions when the price rises. After 5.4, according
to the above figure, the impermanent loss equivalent trend has executed 3
sell orders. The total assets are lower than the total assets without running
the strategy. The rate of return must be less than 8%. This is the so-called
“less profit”, and the less profit is what we call impermanent loss.
If we want to measure the performance of the strategy, we need to get the performance without the impermanent loss, because we only want to know how much money we made through market fluctuations. First, the impermanent loss opening volume, that is, the opening volume caused by price changes is:
- Arithmetic posAvg = exp(0.5log(startPricecurrentPrice))
- Geometric posAvg = (startPrice + currentPrice)/2
In this case, how much the base and quote are increased or decreased:
- base = (initBase + unilateral) * currentPrice
- quote = initQuote - unilateral * posAvg
- theroyEquity = base + quote. // Current net worth for impermanent loss simulation
The equity at the end of the strategy:
- finalEquity = finalBase*currentPrice + finalQuote The equity at the start:
- initEquity = initBase*startPrice + initQuote
Performance without impermanent losses
- (finalEquity - theroyEquity)/initEquity/totalDays*365
Performance with impermanent losses
- (finalEquity - initEquity)/initEquity/totalDays*356
Situation where we need to use market orders
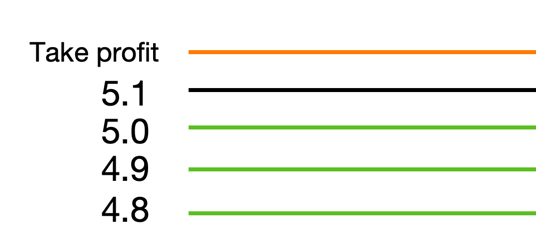
When prices move too quickly, there is a chance that it will be too late to fill the order, as shown below:
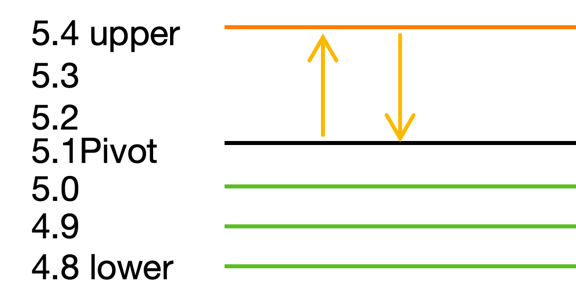 The price pins upwards and then immediately returns. The sell orders at
5.2 and 5.3 are filled, but the strategy does not fill the buy orders in time,
and the price returns to 5.1. At this point, there is a gap between the position
and the target position, and in order to close this gap, we need to buy back
the missing position at 5.1. It is worth noting that the market fill is beneficial
to the strategy because the market fill gives us a more advantageous average price.
The price pins upwards and then immediately returns. The sell orders at
5.2 and 5.3 are filled, but the strategy does not fill the buy orders in time,
and the price returns to 5.1. At this point, there is a gap between the position
and the target position, and in order to close this gap, we need to buy back
the missing position at 5.1. It is worth noting that the market fill is beneficial
to the strategy because the market fill gives us a more advantageous average price.
As in the above chart, if the fill order is timely, it will buy back 5.3, 5.2 when the position reaches 5.1, the average price of the position is (5.1 + 5.2 + 5.3)/3 = 5.2, if the position is not filled in a timely manner, it will be filled at the market price of 5.1, the cost of 5.1, 5.1 < 5.2, the strategy to get a lower cost of ownership of the position.
Grid trading strategy that doesn’t have a price pivots
The above mentioned grid strategy, the price pivot is fixed, this type of grid is more limited, because if you want to make a profit, the price must fluctuate around the established grid pivot, and the grid has a clear upper and lower bounds, breaking through the upper and lower bounds, the strategy will be in a “full position”, can not be traded.
In order to solve this problem, the grid strategy and extend the grid strategy
without price pivot, also known as the dynamic pivot grid strategy,
which is similar to the Martin strategy, in the beginning of the strategy,
buy a position, in accordance with the direction of the position to hang
a number of current price single, single volume depends on the mode of addition,
in the opposite direction of the position is hung on the take-profit single,
whenever the direction of the position of the limit order transaction, the
average price of the position and the volume of the position change, the
take-profit single change operation. Take-profit order to change the order operation.
The pseudo-code is as follows:
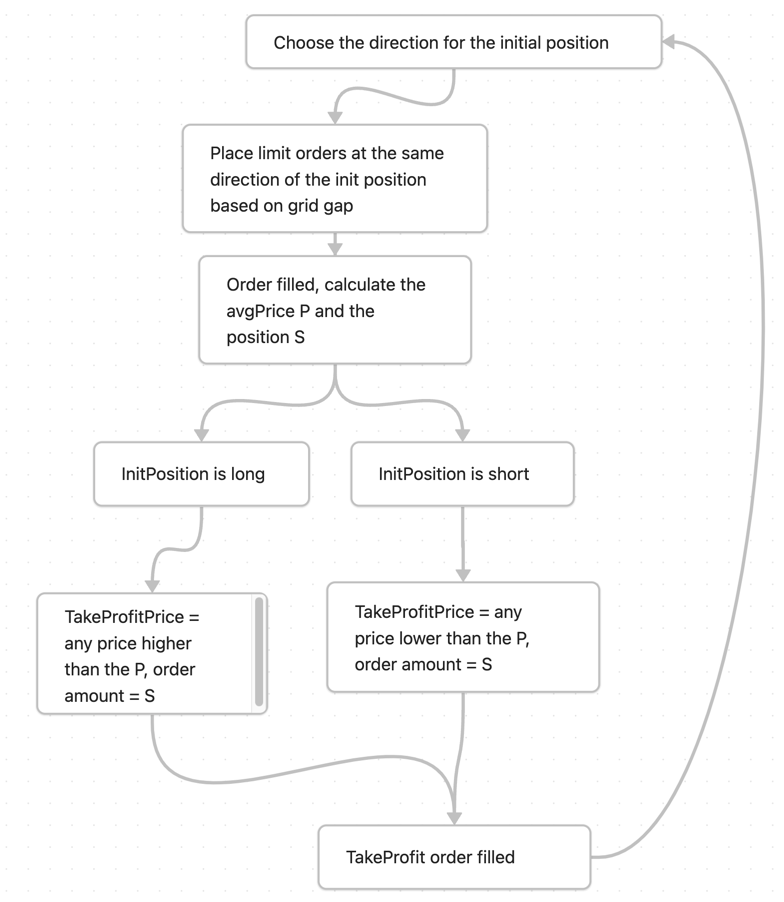 After each take profit order is filled, the price at which the position is bought
is the new pivot, which is where the Dynamic Pivot Grid comes from. It is
worth noting that this grid can choose to do two-way.
After each take profit order is filled, the price at which the position is bought
is the new pivot, which is where the Dynamic Pivot Grid comes from. It is
worth noting that this grid can choose to do two-way.
- situation where the initial position is long:
- situation where the initial position is short:

Strategy in practice
Margin call
To successfully place a limit buy or sell order, you need to have sufficient margin. In spot trading, taking ETHBTC as an example, a buy order requires BTC as margin, and a sell order requires ETH as margin. If the margin is insufficient, the exchange will report an insufficient balance error. In general, according to the formula, all grids can be filled from the upper bound to the lower bound (all margin is used up), but sometimes due to system errors such as calculation inaccuracy, the margin may be insufficient.
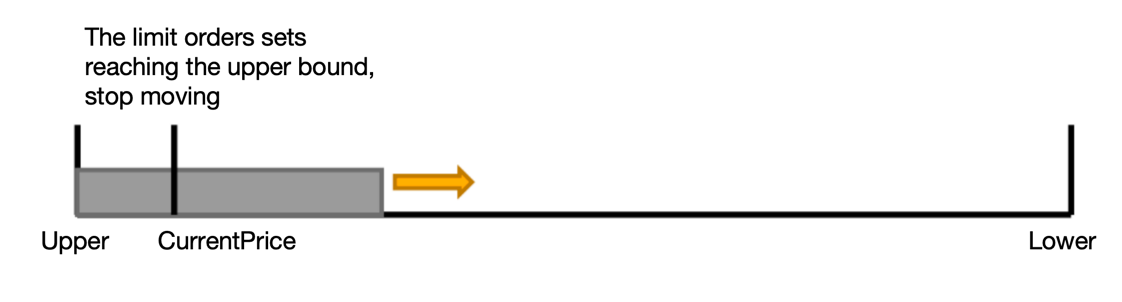
Therefore, in order to avoid this situation, we can choose to place orders only around the current price,
and there is no need to place orders from the upper limit to the lower limit. As shown in the following figure:
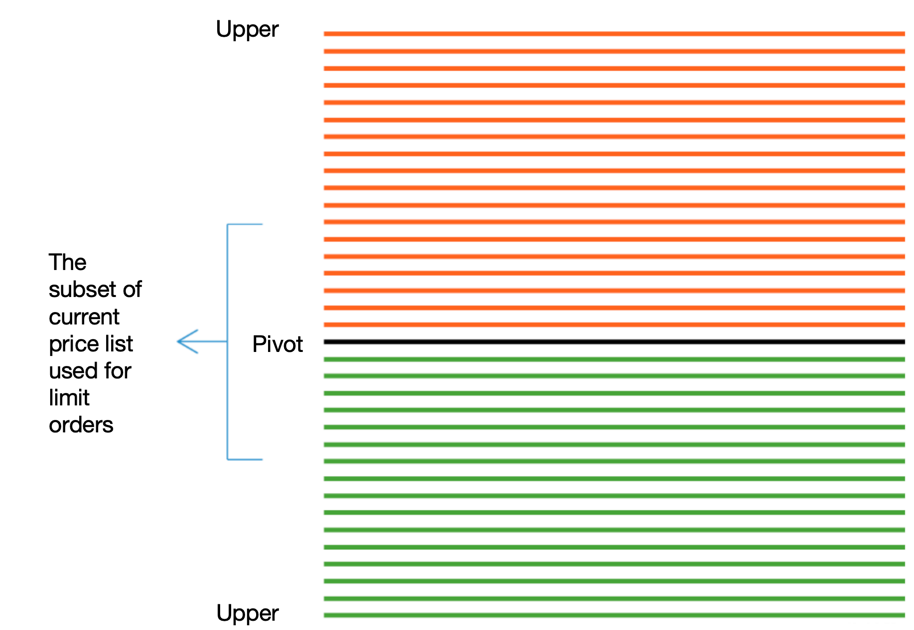 This way you can perfectly avoid the situation of insufficient margin.
This way you can perfectly avoid the situation of insufficient margin.
Price list maintaining
Assuming there are 1000 grids or 1000 prices from the upper bound to the lower bound,
we select 100 grids around the current price as the order range. These 100
prices are a subset of the 1000 prices and move with the current price.
Generally, we place 50 buy orders and 50 sell orders.
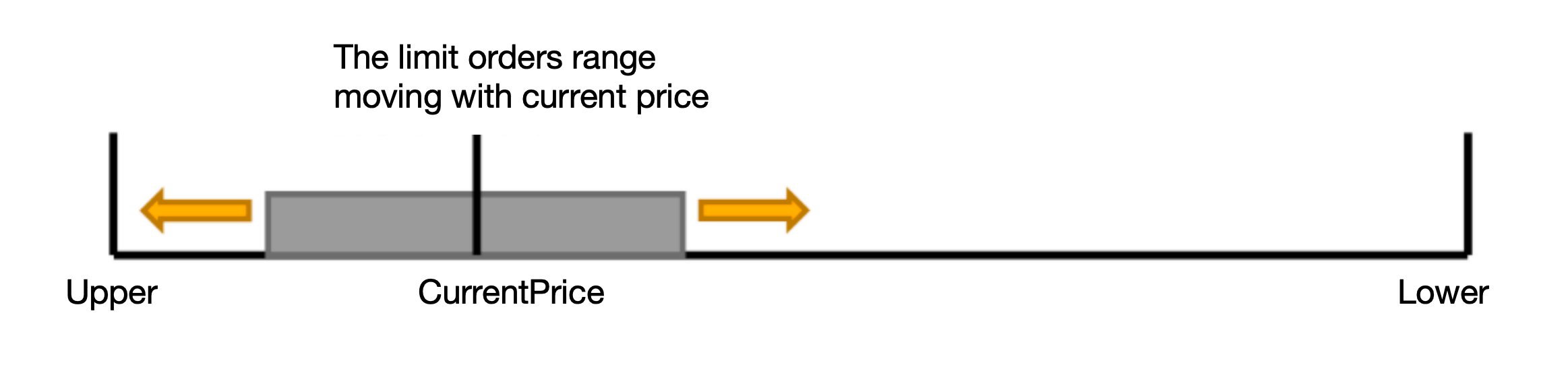 When one of the 100 prices touches the boundary, the order range no longer needs to be changed:
When one of the 100 prices touches the boundary, the order range no longer needs to be changed:
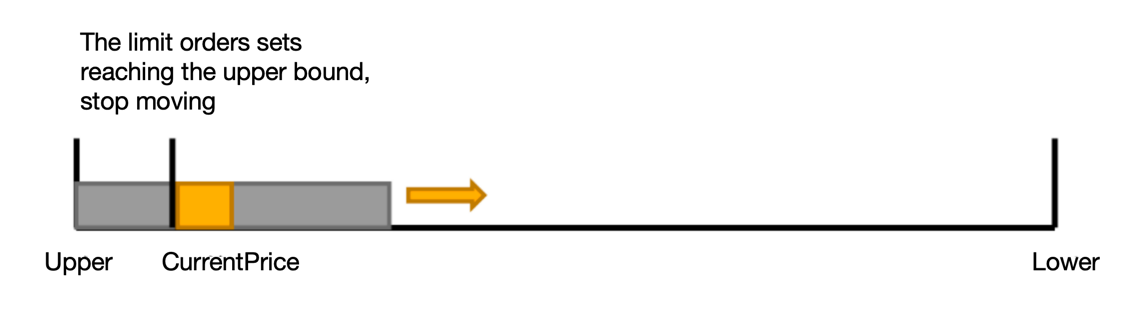
 At this time, the number of buy and sell orders is not equal, as shown in the figure, there are about 30 sell orders and 70 buy orders.
At this time, the number of buy and sell orders is not equal, as shown in the figure, there are about 30 sell orders and 70 buy orders.
Order replenishment
The order-filling mechanism is very simple. It only requires periodic checking
(once every 0.5 seconds) of the price list of online pending orders and the
price list maintained locally by our strategy, and making a difference between
the two lists (the difference is also a price list). The result is the price list we need to fill the order:
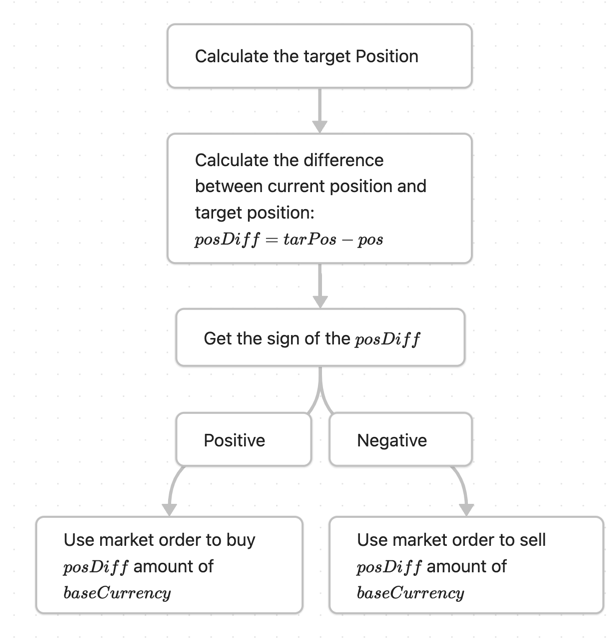
Market order for replenishment
The market price margin mechanism needs to use the formula given above
to calculate the target position tarPos, and then use tarPos to make a difference
with the current position. If the difference is greater than 0, it means selling at the market price.
Code
This code is based on VNPY, which is available under the MIT License.
- Price list maintaining
def update_grid_price(self):
if not self.last_trade_price:
tick = self.get_tick(self.vt_symbol)
if not tick:
return
current_price = tick.last_price
else:
current_price = self.last_trade_price
msg = f"开始更新区间"
self.write_log(msg)
sideLength = self.side_grid_amount
midIndex = self.find_current_level(current_price)
right = len(self.grid_price[midIndex:]) - 1
left = len(self.grid_price[:midIndex])
if left <= self.side_grid_amount:
msg = f"区间已覆盖下界:{self.lower_price}, 不需要更新区间"
self.write_log(msg)
if self.grid_price_range:
return
if right <= self.side_grid_amount:
msg = f"区间已覆盖上界:{self.upper_price}, 不需要更新区间"
self.write_log(msg)
if self.grid_price_range:
return
buy_count = 0
sell_count = 0
for ID in list(self.active_orders.keys()):
order:OrderData = self.active_orders[ID]
if order.vt_symbol == self.vt_symbol:
if order.direction == Direction.LONG:
buy_count+=1
else:
sell_count+=1
if buy_count <= 20 or sell_count <= 20 or True:
if right >= sideLength and left >= sideLength:
startIndex = midIndex - sideLength
endIndex = midIndex + sideLength
elif right < sideLength:
endIndex = len(self.grid_price) - 1
startIndex = midIndex - sideLength - (sideLength - right)
else:
startIndex = 0
endIndex = midIndex + sideLength + (sideLength - left)
if self.grid_price_range:
old_range = self.grid_price_range
self.grid_price_range = self.grid_price[startIndex: endIndex+1]
old_left = list(set(old_range) - set(self.grid_price_range)) # 要撤的单
# new_left = list(set(old_range) - set(self.grid_price_range)) # 要下的单, 不需要处理,由replenish_grid处理
# 找出old_left中的所有价格的key
cancel_index = []
for vt_orderId in list(self.active_orders.keys()):
order = self.active_orders[vt_orderId]
price = formatPoint(order.price, self.tick_size)
if price in old_left:
cancel_index.append(vt_orderId)
if len(cancel_index) == 0:return
self.batch_cancel(cancel_index)
else:
self.grid_price_range = self.grid_price[startIndex: endIndex+1]
else:
msg = f"买单{buy_count}, 卖单{sell_count},足够,不需要更新区间"
self.write_log(msg)
- order replenishment
def replenish_grid(self):
""""""
if not self.grid_price_range:
return
tick : TickData = self.get_tick(self.vt_symbol)
current_price = tick.last_price
msg = f"{datetime.datetime.now()}:开始填充网格"
self.write_log(msg)
online_price_list = []
for vt_orderId in list(self.active_orders.keys()):
order:OrderData = self.active_orders[vt_orderId]
if order.vt_symbol != self.vt_symbol:
continue
price = formatPoint(order.price, self.tick_size)
online_price_list.append(price)
# 找出未填充的网格
diff = list(set(self.grid_price_range) - set(online_price_list))
self.write_log(f"差集{diff}, 订单数量{len(self.active_orders)}")
reqs = []
if not self.last_trade_price:
self.last_trade_price = current_price
if not self.replenish_flag:
self.replenish_flag = True
else:
msg = "下单函数正在执行"
self.write_log(msg)
return
for price in diff:
price = float(price)
if price == self.last_trade_price:
self.write_log(f"网格:{formatPoint(price, self.tick_size)},处于当前level,不补单")
continue
if self.contract_type == '现货':
volume = self.grid_amount
else:
if self.margin == '反向':
volume = self.grid_volume
else:
volume = self.get_grid_volume(price)
if float(price) < self.last_trade_price:
reqs.append({
'vt_symbol': self.vt_symbol,
'price': formatPoint(price, self.tick_size),
'volume': volume,
'order_type': OrderType.POSTONLY,
'direction': Direction.LONG,
'offset': Offset.NONE
})
else:
reqs.append({
'vt_symbol': self.vt_symbol,
'price': formatPoint(price, self.tick_size),
'volume': volume,
'order_type': OrderType.POSTONLY,
'direction': Direction.SHORT,
'offset': Offset.NONE
})
if len(reqs) > 0:
if len(reqs) > 100:
self.batch_order(self.vt_symbol, reqs[:100])
else:
self.batch_order(self.vt_symbol, reqs)
self.replenish_flag = False
- Market order for replenishment
def regular_rebalance(self):
is_refill = False
tick: TickData = self.get_tick(self.vt_symbol)
current_price = tick.last_price
if current_price > self.upper_price or current_price < self.lower_price:
print(
f"{datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}:现价:{current_price}, 超过网格上界:{self.upper_price}或下界:{self.lower_price},")
return
current_price = self.last_trade_price
if not self.last_trade_price:
current_price = tick.last_price
actual_pos = self.pos
if self.contract_type == '现货':
if not self.equal_gap:
actual_pos = self.pos # 现在有多少现货
self.virtual_tar_pos = (math.log(self.init_price / current_price) / math.log(1 + self.grid_step)) * float(
self.grid_amount) + self.init_amount / 2 # 目标仓位有多少base currency
actual_tar_pos = self.leverage * (self.virtual_tar_pos)
else:
# 等差现货
actual_pos = self.pos # 现在有多少现货
self.virtual_tar_pos = int((self.init_price - current_price)/self.contract.pricetick)*float(self.grid_amount) + self.init_amount / 2
actual_tar_pos = self.leverage * (self.virtual_tar_pos)
else:
if self.gateway_name == 'OUYI':
if self.margin == '反向':
self.virtual_tar_pos = (math.log(self.init_price / current_price) / math.log(
1 + self.grid_step)) * self.grid_volume # 目标仓位有多少张
actual_tar_pos = self.leverage * (self.virtual_tar_pos)
else:
self.virtual_tar_pos = (math.log(self.init_price / current_price) / math.log(
1 + self.grid_step)) * self.grid_amount / (self.contract_val * current_price) # 目标仓位有多少张
actual_tar_pos = self.leverage * (self.virtual_tar_pos)
if self.gateway_name == "BIAN":
self.virtual_tar_pos = (math.log(self.init_price / current_price) / math.log(
1 + self.grid_step)) * self.grid_amount / (current_price) # 目标仓位有多少张
actual_tar_pos = self.leverage * (self.virtual_tar_pos)
if actual_pos > actual_tar_pos:
if self.contract_type == '现货':
pos_diff = actual_pos - actual_tar_pos
msg = f"与目标仓位差{pos_diff / float(self.grid_amount)}个网格"
self.write_log(msg)
if pos_diff / float(self.grid_amount) >= 3:
pos_diff = formatPoint(actual_pos - actual_tar_pos, self.min_size)
is_refill = True
elif self.margin == '反向':
pos_diff = actual_pos - actual_tar_pos
msg = f"与目标仓位差{pos_diff / float(self.grid_volume)}个网格"
self.write_log(msg)
if pos_diff / self.grid_volume >= 3:
is_refill = True
else:
if self.gateway_name == 'OUYI':
pos_diff = actual_pos - actual_tar_pos
msg = f"与目标仓位差{pos_diff*self.contract_val*current_price / self.grid_amount}个网格"
self.write_log(msg)
if pos_diff*self.contract_val*current_price / self.grid_amount >= 3:
is_refill = True
else:
pos_diff = actual_pos - actual_tar_pos
msg = f"与目标仓位差{pos_diff*current_price / self.grid_amount}个网格"
self.write_log(msg)
if pos_diff*current_price / self.grid_amount >= 3:
is_refill = True
if is_refill:
msg = f"开始补仓: {pos_diff}"
self.write_log(msg)
self.restart_orderId = self.sell(
vt_symbol=self.vt_symbol,
price=formatPoint(tick.bid_price_5, self.tick_size),
volume=pos_diff,
order_type=OrderType.LIMIT
)
elif actual_pos < actual_tar_pos:
if self.contract_type == '现货':
pos_diff = actual_tar_pos - actual_pos
msg = f"与目标仓位差{pos_diff / float(self.grid_amount)}个网格"
self.write_log(msg)
if pos_diff / float(self.grid_amount) >= 3:
pos_diff = formatPoint(actual_tar_pos - actual_pos, self.min_size)
is_refill = True
elif self.margin == '反向':
pos_diff = actual_tar_pos - actual_pos
msg = f"与目标仓位差{pos_diff / float(self.grid_volume)}个网格"
self.write_log(msg)
if pos_diff / self.grid_volume >= 3:
is_refill = True
else:
if self.gateway_name == 'OUYI':
pos_diff = actual_tar_pos - actual_pos
msg = f"与目标仓位差{pos_diff * self.contract_val * current_price / self.grid_amount}个网格,不需补仓"
self.write_log(msg)
if pos_diff * self.contract_val * current_price / self.grid_amount >= 3:
is_refill = True
else:
pos_diff = actual_tar_pos - actual_pos
msg = f"与目标仓位差{pos_diff * current_price / self.grid_amount}个网格"
self.write_log(msg)
if pos_diff * current_price / self.grid_amount >= 3:
is_refill = True
if is_refill:
msg = f"开始补仓: {pos_diff}"
self.write_log(msg)
self.restart_orderId = self.buy(
vt_symbol=self.vt_symbol,
price=formatPoint(tick.ask_price_5, self.tick_size),
volume=pos_diff,
order_type=OrderType.LIMIT
)
else:
print(f"{datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}: 无需补仓")